linux时间和API
linux时间和API
0 前言
PHC 是 PTP 硬件时钟,用于高精度时间同步(纳秒级)。 RTC 是 主板硬件时钟,用于基础时间维护(毫秒级)。 通过 ls /sys/class/ptp/ 和 ethtool -T eth0 可检查 PHC 支持
1 时间
1.1 硬件时间(RTC时间)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 查询硬件时间
hwclock --show
# 将系统时间设置为硬件时间
hwclock --systohc
# 将硬件时间设置为系统时间
hwclock --hctosys
1.2 系统时间(UTC时间)
1
2
3
4
5
# 查询系统时间(UTC)
date -u
# 查询本地时间(由系统时间UTC和时区共同决定)
date
1.3 本地时间
1
2
# 查询本地时间(由系统时间UTC和时区共同决定)
date
1.4 PHC时间
install linuxptp tools and run phc_ctl
1
sudo apt install linuxptp
1
2
sudo phc_ctl /dev/ptp1 get
phc_ctl[31856.285]: clock time is 1751998409.995321853 or Wed Jul 9 02:13:29 2025
2 API
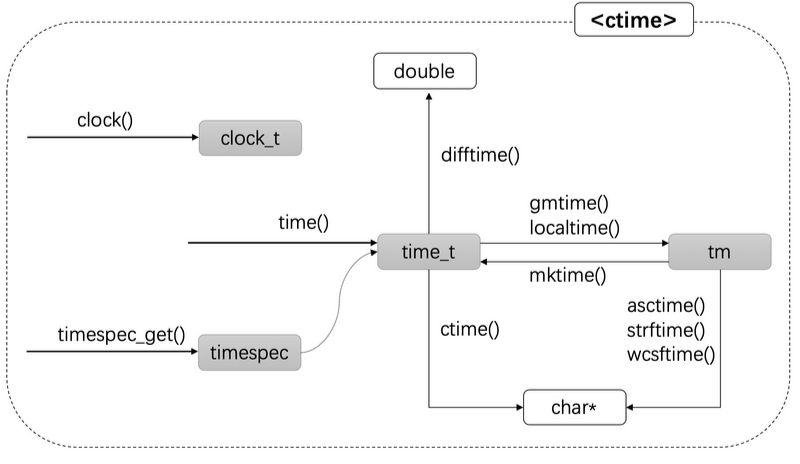
2.1 C Stype API
| 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| time_t | 从纪元起的时间类型 |
| tm | 日历时间类型 |
| timespec∗ | 以秒和纳秒表示的时间 |
| clock_t | 进程运行时间 |
- tm是日历类型,因为它其中包含了年月日等信息. 通过gmtime,localtime和mktime函数可以将time_t和tm类型互相转换
- 考虑到时区的差异,因此存在gmtime和localtime两个函数
2.2 CPP11
chrono库:C++ 11中新增API,增加了时间点,时长和时钟等相关接口
时钟
为了满足不同类型的需求,C++11 chrono库中包含了三种类型的时钟,它们的说明如下:
- system_clock 系统时钟
- steady_clock 单调时钟,不会被调整
- high_resolution_clock 拥有可用的最短嘀嗒周期的时钟
system_clock 的时间来源是系统时钟,而系统时间随时都可能被调整。所以如果你需要计算两个时间点的时间差,这不是一个好的选择。因为如果两次时间差中间系统时间被调整了,其结果就没有意义了。
steady_clock会保证单调性。它就好像物理时间只会向前移动,无法减少。它最适合用来度量间隔。
high_resolution_clock 表示实现提供的拥有最小计次周期的时钟。它可以是 system_clock 或 steady_clock 的别名,也可能是第三个独立时钟。
这三个时钟类有一些共同的成员
| 成员名 | 类型/说明 |
|---|---|
| now() | 静态成员函数,返回当前时间,类型为 clock::time_point |
| time_point | 成员类型,当前时钟的时间点类型,见下文“时间点” |
| duration | 成员类型,时钟的时长类型 |
| rep | 成员类型,时钟的 tick 类型,等同于 clock::duration::rep |
| period | 成员类型,时钟的单位,等同于 clock::duration::period |
| is_steady | 静态成员类型,是否是稳定时钟,对于 steady_clock 该值一定为 true |
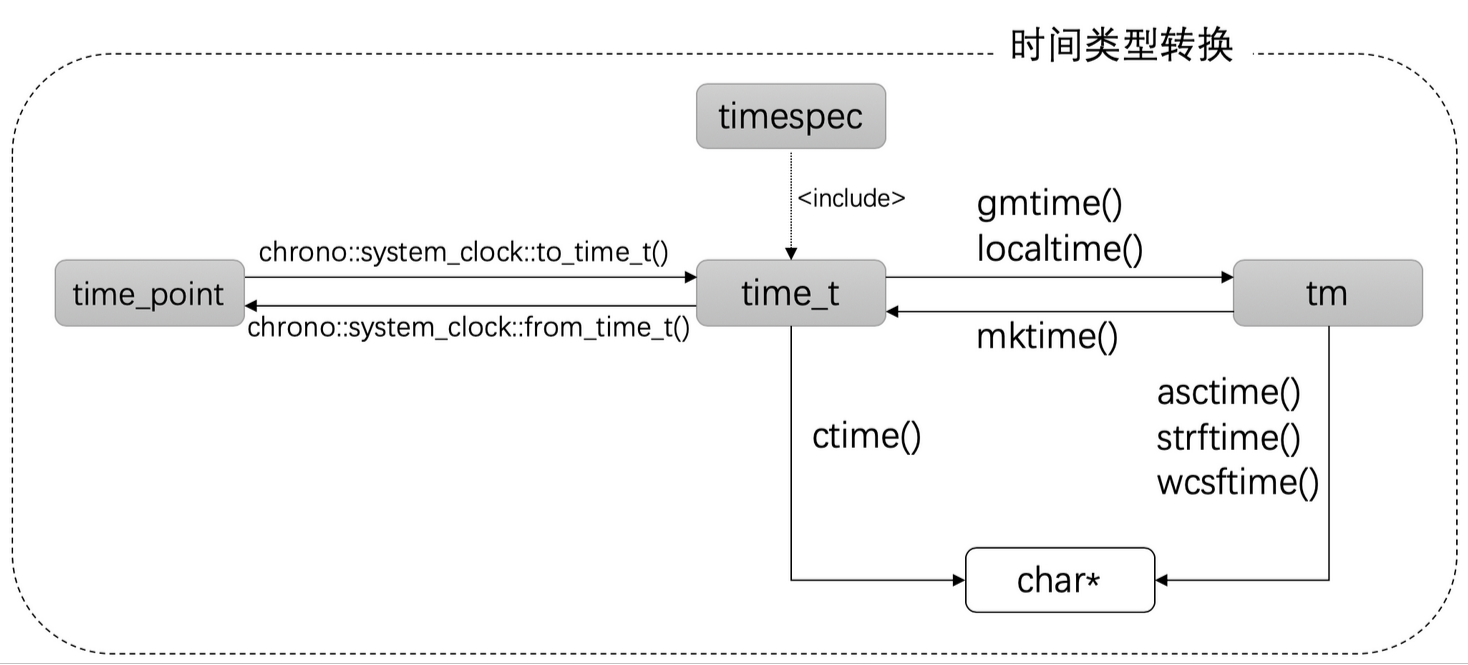
system_clock与另外两个clock不一样的地方在于,它还提供了两个静态函数用来与std::time_t来回转换
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| to_time_t | 转换系统时钟时间点为 std::time_t |
| from_time_t | 转换 std::time_t 到系统时钟时间点 |
1
2
3
auto now = chrono::system_clock::now();
time_t time = chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(now);
cout << "Now is: " << ctime(&time) << endl;
时长
1
auto timestamp = now.time_since_epoch().count();
这里time_since_epoch()的返回值是类型是时间长度(duration类型),即从纪元起点到now对应时间点间的时间长度。时间长度类型可以通过count()转化为数值类型,方便进一步在其他代码中使用
时间点
时间点中包含了时钟和时长两个信息
1
2
const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::steady_clock> start =
std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
references
- https://zh.cppreference.com/w/c/header/time.html
- https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/header/ctime.html
- https://zh.cppreference.com/w/cpp/header/chrono.html
- https://paul.pub/cpp-date-time/
- https://getiot.tech/linux-command/phc_ctl/
- https://linuxkernel.org.cn/doc/html/latest/driver-api/ptp.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/Dontla/article/details/133975639
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.